Într -o epocă în care progresele biotehnologiei împing granițele sănătății umane și longevității, Transplantul autolog a apărut ca o strategie promițătoare. Această tehnică inovatoare perturbă domeniul regenerării organelor, oferind o cale potențială pentru a extinde semnificativ durata de viață a omului. Acest articol va explora implicațiile transplantului autolog pentru extinderea vieții, the role of biotechnology centers in advancing this technology, and the potential future of a 150-year lifespan for humanity.
Understanding Autologous Transplantation
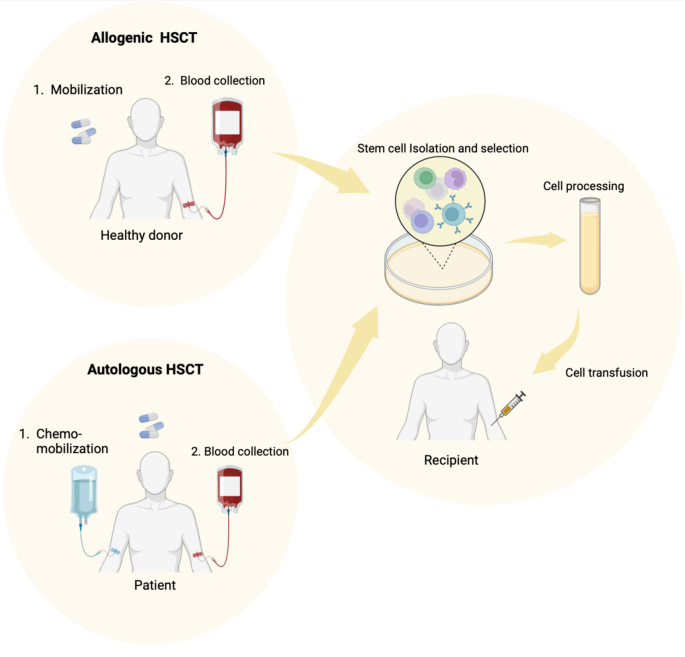
Autologous transplantation is a process where cells, tissues, or even organs are removed from an individual, cultivated or modified, and then re-introduced into the same individual. This technique leverages the body’s natural regenerative capabilities, reducing the risk of organ rejection and eliminating the need for life-long immunosuppression, which is commonly associated with allogeneic transplantation (transplants from a different donor).
The Role of Stem Cells in Autologous Transplantation
Celule stem, the building blocks of all tissues and organs in the body, play a central role in autologous transplantation. These cells have the unique ability to self-renew and differentiate into any cell type, making them invaluable in the process of organ regeneration.
There are two main types of stem cells used in autologous transplantation:
-
- Celule stem embrionare (ESC): These are derived from early-stage embryos and have the potential to develop into any cell type in the body.
- Celule stem adulte (ASCS): These are found in various tissues throughout the body and have a more limited range of differentiation.
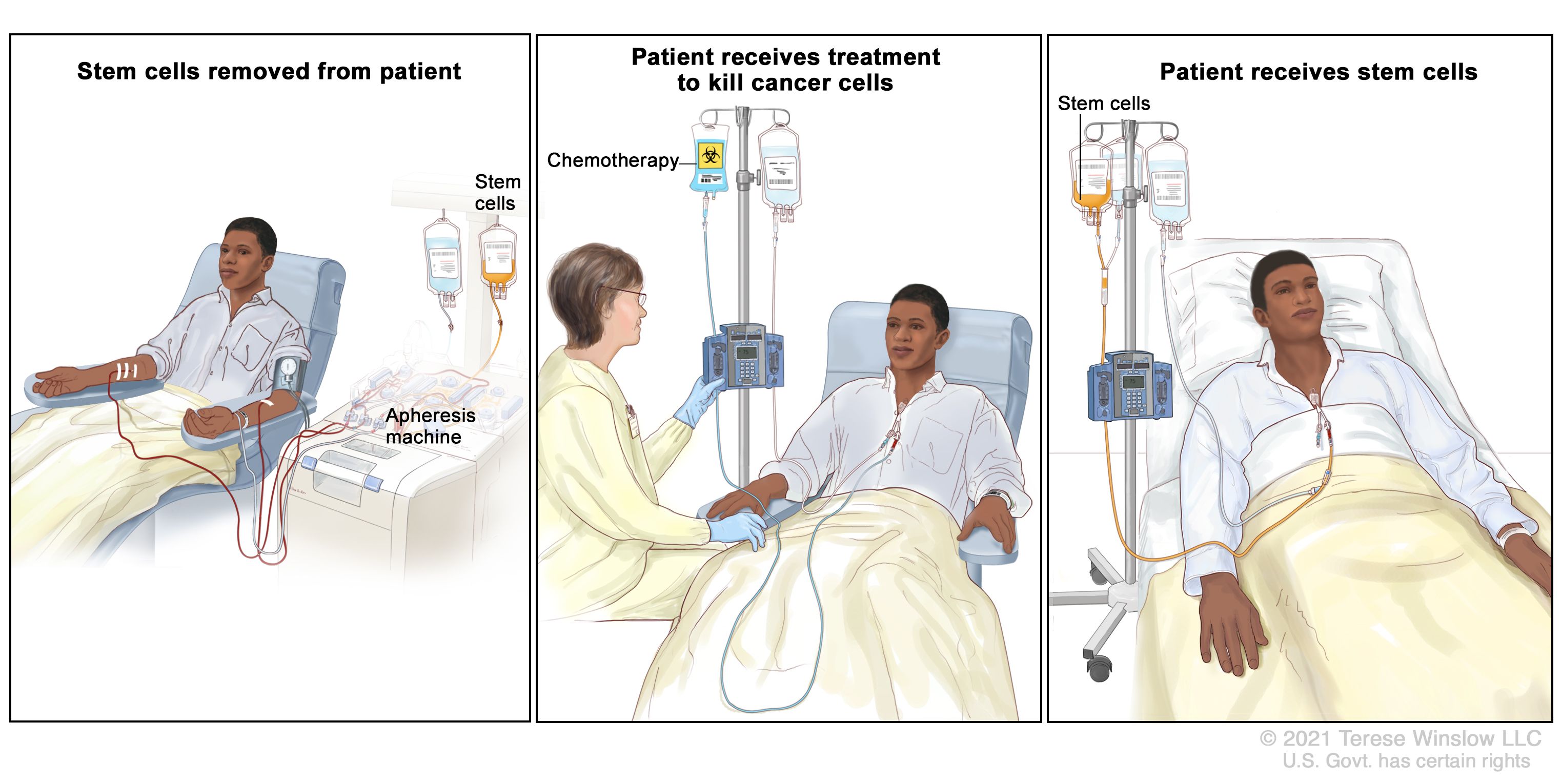
Autologous transplantation primarily utilizes adult stem cells, harvested from the patient’s own body, thus minimizing the risk of immune rejection.

Biotechnology Centers: A Hub for Advancing Autologous Transplantation
Biotechnology centers are at the forefront of research and development in autologous transplantation. These institutions are pioneering advancements in stem cell biology, tissue engineering, și medicină regenerativă, all of which are fundamental to the success of autologous transplantation.
Key roles of biotechnology centers in advancing autologous transplantation include:
-
- Research & Dezvoltare: Biotech centers conduct groundbreaking research to improve the efficiency of stem cell extraction, cultivation, și transplant.
- Studii clinice: These centers often run clinical trials to test the safety and efficacy of new procedures and technologies.
- Education & Training: Biotech centers educate healthcare professionals and the public about the benefits and potential risks of autologous transplantation.
- Policy Advocacy: They also play a role in influencing healthcare policies, ensuring that the potential of autologous transplantation is fully realized.

Autologous Transplantation for Life Extension
Aging is a complex process involving the gradual deterioration of body functions, often leading to chronic diseases and eventual death. Transplant autolog, through its potential for organ regeneration, offers a promising avenue for life extension.
Regenerarea organelor: A Pathway to Longevity
One of the key promises of autologous transplantation is the potential for organ regeneration. With age, our organs naturally lose their functionality. Cu toate acestea, through the use of stem cells, it’s possible to replace damaged cells and tissues, effectively regenerating the organ and restoring its function.
Research has shown promising results in the regeneration of various organs, including the heart, ficat, și rinichi. In fact, some biotechnology centers are already offering therapies for heart repair, utilizing the patient’s own stem cells to regenerate damaged heart tissue.
The 150-Year Lifespan: A Future Possibility?
Given the potential of autologous transplantation in organ regeneration, it’s reasonable to speculate about a future where humans could live up to 150 years or even more. The concept of a 150-year lifespan is not just a fantasy; some scientists believe it could be a reality within the next few decades.
Cu toate acestea, extending human lifespan to 150 years involves more than just organ regeneration. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the aging process, including the genetic, cellular, and molecular mechanisms involved. În plus, ethical, social, and economic implications of such longevity must be considered.
Concluzie: The Future of Autologous Transplantation in Longevity
Transplant autolog, with its potential for organ regeneration, is revolutionizing the field of longevity research. Biotechnology centers worldwide are facilitating this progress, advancing our understanding of stem cells, and developing innovative therapies that could extend human lifespan.
While the prospect of a 150-year lifespan remains speculative, the advancements in autologous transplantation bring us a step closer to this reality. Pe măsură ce cercetarea continuă, we can anticipate further breakthroughs that could redefine the limits of human longevity.
Are you interested in learning more about the potential of autologous transplantation for life extension? Are you considering investing in this cutting-edge biotechnology? Book your consultation at a top longevity biotechnology center today and take a step towards the future of human health and longevity.